

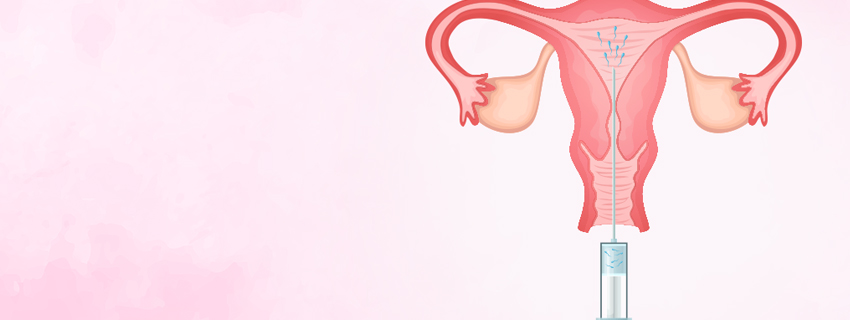
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment where sperm is directly placed into a woman's uterus to facilitate fertilization. Here’s a comprehensive overview:
IUI is primarily used to treat infertility in couples where:
IUI is a common fertility treatment that can be effective for many couples struggling with infertility, particularly when the issue is mild to moderate sperm-related or unexplained. It's usually recommended as a first-line treatment before considering more complex procedures like IVF. For personalized advice, consulting a fertility specialist is essential to determine the most suitable treatment approach.